How to Perform a Bare Metal Recovery (BMR) for Linux Machines
A BMR restores the operating system and software applications, and recovers all the backed-up data. BMR is the process of restoring a computer system from bare metal. Bare metal is a computer without any operating system, drivers, and software applications. After the restore is complete, the target machine automatically reboots in the same operating environment as the backup source node and all data is restored.
UDPLinux supports BMR to different hardware. For more information, see How to Create a CentOS-Based Live CD.
A complete BMR is possible because when you back up data, the backup also captures information related to the operating system, installed applications, drivers, and so on.
You can perform a BMR using either of the following options:
- Using the Command line option. For details, view Create a Configuration template Using Command Line.
- Using the IP address or the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the target machine. If you boot the target machine using the Arcserve Unified Data Protection Agent for Linux Live CD, you can get the IP address of the target machine.
Note: Machine can boot up. Only one NIC is configured.
The following diagram displays the process to perform a BMR using the IP or MAC address:
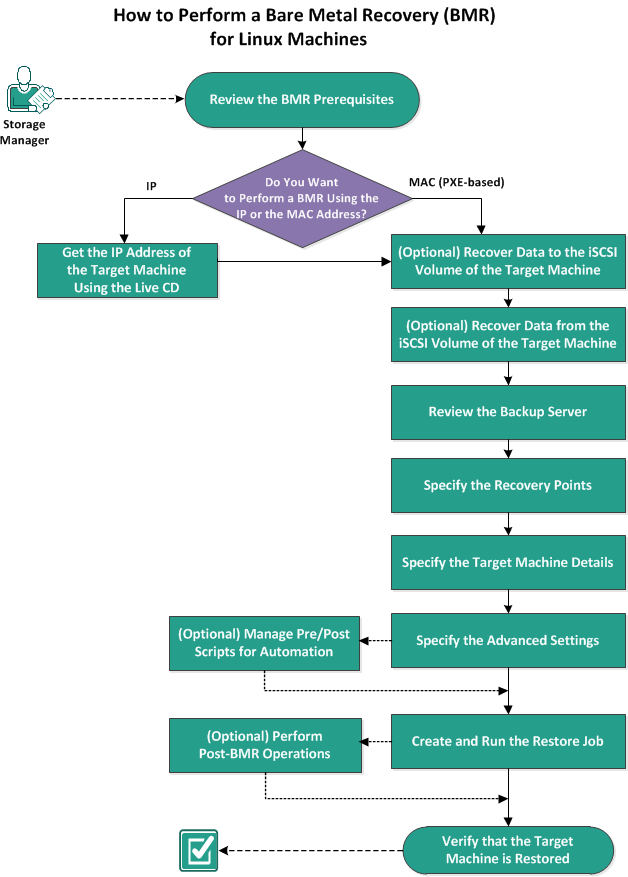
Complete the following tasks to perform a BMR:
- Review the BMR Prerequisites
- Get the IP Address of the Target Machine Using the Live CD
- (Optional) Recover Data to the iSCSI Volume of the Target Machine
- (Optional) Recover Data from the iSCSI Volume to the Target Machine
- Review the Backup Server
- Specify the Recovery Points
- Specify the Target Machine Details
- Specify the Advanced Settings
- (Optional) Manage Pre/Posts Scripts for Automation
- Create and Run the Restore Job
- (Optional) Perform Post-BMR Operations
- Verify that the Target Machine is Restored