Define the Alternate Location Restore Options
During the Restore VM configuration process, specify where the recovered virtual machine is stored. The available selections are Restore to the Original Location and Restore to an Alternative Location.
This procedure explains how to restore a virtual machine to alternate location or different data store.
Follow these steps:
- From the Restore Options dialog, after specifying the Resolve Conflicts and Post Recovery options, select Restore to an Alternative Location.
- For VMware, the Restore Options dialog expands to display additional restore to alternative options.
- For Hyper-V, the Restore Options dialog expands to display additional restore to alternative options.
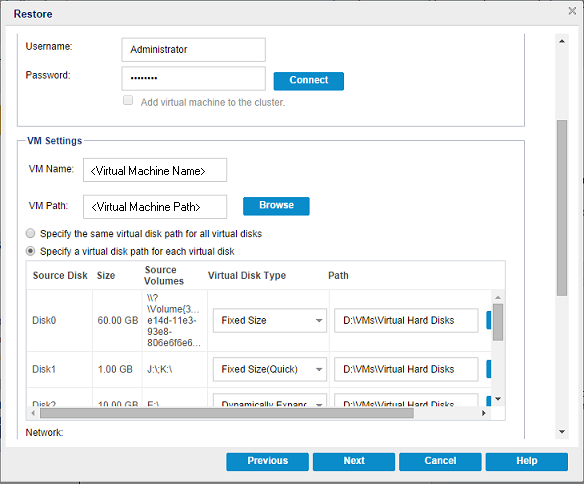
- If you select the Specify a virtual disk path for each virtual disk option, the following dialog appears:
- Specify the appropriate server Information.
- For VMware, enter the following fields:
- For Hyper-V, enter the following fields:
- If you provide the cluster node name as the Hyper-V server name, the check box is disabled and checked by default. As a result, the virtual machine is automatically added into the cluster.
- If you provide the host name of a Hyper-V server that is part of the cluster the check box is enabled and you can select to add the virtual machine into the cluster.
- If you provide the host name of a standalone Hyper-V server that is not part of the cluster the check box is disabled and unchecked.
- When the vCenter/ESX Server Information or Hyper-V Server Information is specified, click the Connect to this vCenter/ESX Server button or click the Connect to this Hyper-V Server button.
- If the alternative server access credential information is correct, the VM Settings fields become enabled.
- Specify the VM Settings.
- For VMware, enter the following fields.
- Virtual Disk Type: Select one of the following options: Thin, Thick Lazy Zeroed, or Thick Eager Zeroed.
- Storage Policy: Select the VM storage policy that is applied to this virtual disk. Select Datastore Default if you do not want to apply the VM storage policy.
- Target Datastore: Select the datastore where the virtual disk is restored.
- For Hyper-V, enter the following fields.
- If you are restoring the virtual machine into Hyper-V cluster and you want the virtual machine to migrate among the cluster nodes, specify the cluster shared volume (CSV) for both- the VM path and the virtual disk path.
- Do not use Fixed Size (Quick) option unless you are sure that earlier you have not saved sensitive information on the storage device where the virtual disk file resides.
- Click OK.
- The Restore Summary dialog opens.
vCenter/ESX Server
Specifies the host name or IP address for the destination vCenter or ESX server system.
Username
Specifies the user name that has access rights to log in to the vCenter/ESX server where you plan to restore the virtual machine.
Password
Specifies the corresponding password for the User Name.
Protocol
Specifies the protocol that you want to use for communication with the destination server. The available selections are HTTP and HTTPS.
Default: HTTPS.
Note: VMware Virtual Disk Development Kit (VDDK) 6.x.x is in-built with Arcserve UDP 6.5 but VDDK 6.x.x does not support HTTP. Make sure to select HTTPS, unless you manually replace the built-in VDDK 6.x.x with another version of VDDK.
Port Number
Specifies the port that you want to use for data transfer between the source server and the destination.
Default: 443.
Hyper-V Server
Displays the host name or IP address for the destination Hyper-V Server system.
Username
Specifies the user name that has access rights to log in to the Hyper-V server where you plan to restore the virtual machine. For Hyper-V cluster VM, specify the domain account that has administrative privilege of the cluster.
Password
Specifies the corresponding password for the User Name.
Add virtual machine to the cluster
Select the option if you want to add the virtual machine that Arcserve UDP restores, into the cluster. Consider the following options:
VM Name
Specifies the virtual machine name that you are restoring.
ESX Server
Specifies the destination ESX server. The drop-down menu contains a listing of all ESX servers that are associated with a vCenter server.
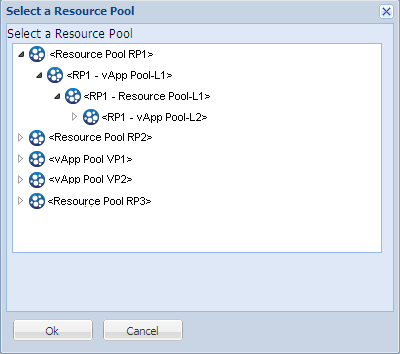
Resource Pool
Selects the Resource Pool or vApp Pool you want to use for the virtual machine recovery.
Note: A Resource Pool is a configured collection of CPU and memory resources. A vApp Pool is a collection of one or more virtual machines that can be managed as a single object.
Default: empty.
Click the Browse Resource Pool button to display the Select a Resource Pool dialog. This dialog contains a listing of all Resource Pools and vApp Pools available for the destination ESX server. Select the pool to use for the virtual machine recovery. You can leave this field blank when you do not want to assign a Resource Pool or vApp Pool to this virtual machine recovery.
Storage Policy
Specify the VM storage policy that is applied to VM home of restored VM. Select Datastore Default if you do not want to apply the VM storage policy.
Note: if you can see only Datastore Default but actually there are other storage policies defined in vCenter, then the account used to connect vCenter does not have enough permission to get the storage policy from vCenter. Verify if the account has the privilege Profile-driven storage view at the vCenter level.
VM DataStore
Specify the destination datastore for VM home of restored VM.
Note: By default, only those datastores that are compatible with selected storage policy are listed. If you want to see all datastores, clear selection of the checkbox Show only compatible datastores for selected storage policy that in under the Disk Datastore table.
Disk Datastore
Specify Virtual Disk Type, Storage Polic,y and Target Datastore for each of the virtual disk of the VM, respectively.
Note: By default only the datastores that are compatible with selected storage policy are listed. If you want to see all datastores, clear selection of the checkbox Show only compatible datastores for selected storage policy that in under the Disk Datastore table.
Network
Specifies the vSphere Standard Switch/vSphere Distributed Switch configuration details.
VM Name
Specifies the virtual machine name that you are restoring.
VM Path
Specifies the destination path (on Hyper-V server) where to save the Hyper-V VM configuration file. The default folder of the VM configuration file for the Hyper-V server is shown by default. You can modify the path directly in the field or click Browse to select one.
Note: If you are restoring the virtual machine into Hyper-V cluster and you want the virtual machine to migrate among the cluster nodes, specify the cluster shared volume (CSV) for both- the VM path and the virtual disk path.
Specify the same virtual disk path for all virtual disks
Specify one path (on Hyper-V server) where to save all virtual disks of the VM together. The default folder of the VM disk file for the Hyper-V server is shown by default. You can modify the path directly in the field or click Browse to select one.
Note: If you are restoring the virtual machine into Hyper-V cluster and you want the virtual machine to migrate among the cluster nodes, specify the cluster shared volume (CSV) for both- the VM path and the virtual disk path.
Specify a virtual disk path for each virtual disks
Specify the path (on Hyper-V server) for each of the virtual disks of the VM respectively. The default folder of the VM disk file for the Hyper-V server is shown by default. You can modify the path directly in the field or click Browse to select one. To assign the virtual disk type, select one of the following options: Fixed Size, Fixed Size (Quick), Dynamically Expanding, and Keep same as Source disk.
Notes:
Fixed Size (Quick)
Using this option, you can restore Fixed Size disk in a quicker way. You do not need to clear unused disk blocks to zero while restoring the disk. However, because of this, some fragments of original data remained on underlying storage. That situation creates risks of information leaks. After the disk is mounted into the virtual machine, the user of the virtual machine may use some disk tools to analyze the raw data in the disk and get the original data on Hyper-V server storage device where the file of virtual disk resides.
Network
Specifies the network configuration details for the VM.
The restore options for alternate location are defined.