

Performing Backups › How the VSS Backup Works
How the VSS Backup Works
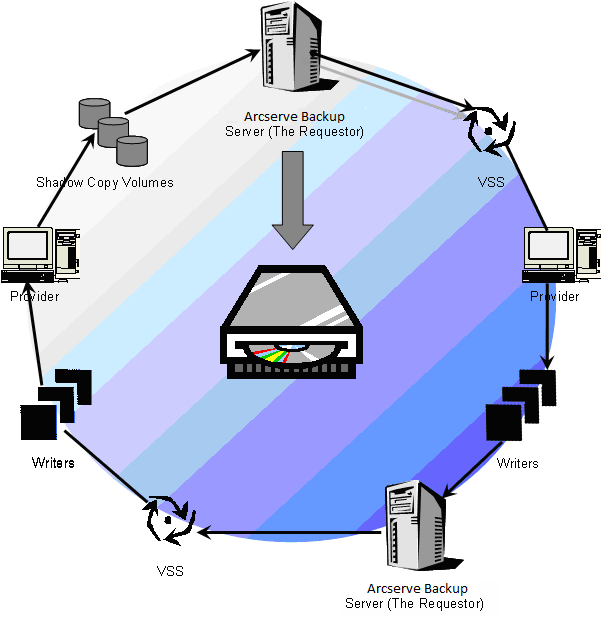
The steps involved in using Arcserve Backup to perform a VSS backup are:
- The Requestor (Arcserve Backup) asks VSS to tell the Writers involved in the backup to gather their writer metadata documents (XML files that contain instructions for the backup) and send them to the Requestor.
Arcserve Backup communicates directly with VSS in local configurations. In remote configurations, the communication between VSS and Arcserve Backup is handled by the Client Agent for Windows, which must be installed on the target computer.
- VSS contacts the Provider responsible for managing the volumes involved in creating the shadow copy. In the simplest case, one Provider is responsible for all of the volumes involved in creating the shadow copy, but in some situations, multiple Providers may be involved.
- VSS contacts the Writers that are part of the backup and asks them to gather their writer metadata documents and send them to the Requestor. The Writers also begin preparing for the freeze by ensuring that the files to be backed up are in a consistent state.
- The Writers send their writer metadata documents to the Requestor. Do not edit these files directly. Use the Backup Manager in Arcserve Backup to indicate the files you want to back up, and the backup and restore methods to use.
- After collecting all the writer metadata documents from the Writers, the Requestor issues another command to VSS, asking it to begin the creation of the shadow copy.
- VSS freezes the Writer's applications, ensuring that the data to be used for the creation of the shadow copy remains consistent and has internal integrity. While an application is frozen, Writers suspend any changes to the files on the original volume, allowing the application and its files to remain available while the shadow copy is created. However, because a VSS backup is a point-in-time backup, any changes made to files after the freeze are not reflected in the shadow copy and are not backed up.
- VSS issues a command to the Provider, telling it to create a shadow copy of the current disk state.
- The Provider creates the shadow copy on the shadow copy volume.
- VSS thaws the frozen Writers, returning them to their normal state. Any changes that were queued by the Writer while the shadow copy was being created are written to the original volume at this time. The thaw occurs after the shadow copy has been created and before the data is backed up. This allows the applications to start using the original volumes while the backup is made using the shadow copy volume.
- The backup data is sent to the Requestor (Arcserve Backup) by the Client Agent for Windows.
- The Requestor backs up the data to media. The Writer metadata is stored with the shadow copy data so that recovery information is available when the data is restored.
Copyright © 2015 .
All rights reserved.
 
|
|


