

For mission-critical applications deployed into a cluster environment, the data is the most valuable investment and protection of this data is essential. A cluster environment always involves multiple physical nodes, a virtual name/IP address, and cluster-specific applications, all of which bring additional complexities for the backup and restore application. To address these complexities, Arcserve Backup provides multiple backup and restore capabilities for servers operating in a cluster environment.
Note: Arcserve Backup supports cluster environments for Microsoft Cluster Server (MSCS) and NEC Cluster Server (CLUSTERPRO/ExpressCluster).
The following diagram shows a typical active/passive cluster environment. The active node in this cluster is associated with two names and IP addresses: one for the physical name of the machine and the other for the virtual name created by the cluster itself or the cluster-aware application. The passive node is associated with only one name, the physical name of the machine. To fully protect the cluster, you need to install the Arcserve Backup agent into both of these physical nodes. In each of these instances, depending on the protected target, Arcserve Backup will be deployed to protect your cluster and back up your data using either the physical node or the virtual node.
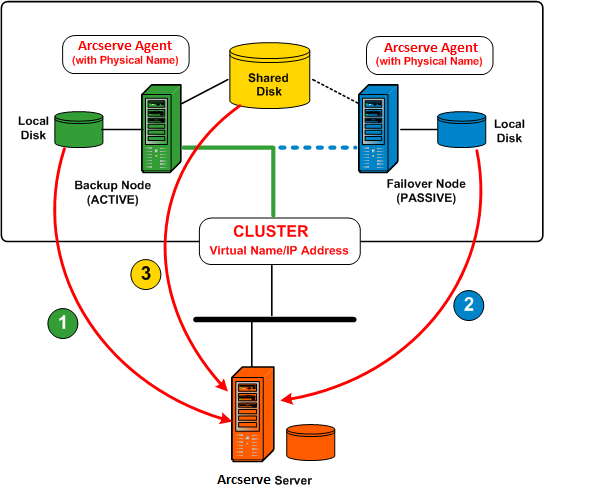
To protect the system state of each cluster node and the local application data, you need to schedule the backup job based on the physical name/IP address of the machine. For the active node (1), you can back up all attached disks, including the local disks as well as shared disks. For a passive node (2), you can only back up the local disks. However, it is not a best practice to back up a shared disk based only on physical name. In a cluster environment, the role of each node (active and passive) may change dynamically due to a failover condition. If you specify the physical name of the failed node, the backup will fail and the data that is located on the shared disk will not be backed up.
In a cluster-aware application (SQL Server cluster or MS Exchange cluster), all data is saved on a shared disk to provide HA capability. To back up this data, the Arcserve Backup agent (installed on each physical node) will archive the data into the shared disk via the virtual name and IP address of the cluster (3). Under normal conditions, Arcserve Backup will back up data from the shared disk using the virtual name and IP address of the cluster as the source rather than the physical name and IP address of the active node. The advantage of doing this is if the active node fails or is shut down, the failover mechanism of cluster will make the passive node become the new active node, and Arcserve Backup will automatically continue to perform backups from the shared disk. As a result, you can schedule rotation backup jobs to protect your data located in the shared disk regardless which cluster node is active.
Note: To back up any application specified data (for instance, a SQL Server database), you should deploy the corresponding Arcserve Backup agent and perform the backup using the virtual name associated with this cluster-aware application.
|
Copyright © 2017 |
|