

To prevent the accidental overwriting of needed data, Arcserve Backup manages media for rotation schemes in media pools. Media pools are logical collections of rewriteable, removable storage media managed as a single unit.
Important! Deduplication and Cloud devices cannot be assigned to media pools.
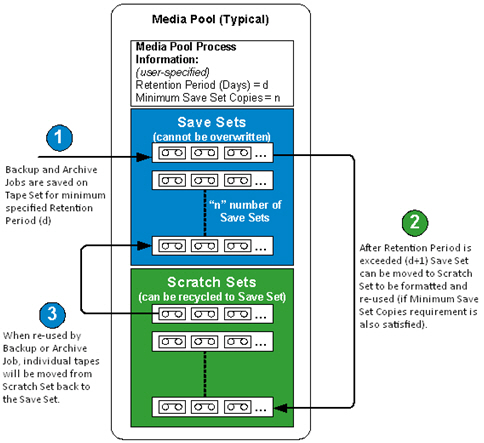
A media pool is a collection of backup and archive media (tapes) that is set aside for a specific job and managed as a unit. A media pool is a set of tapes that is logically grouped and used exclusively for a particular recurring backup and archive job. Within Arcserve Backup each media pool is automatically divided into a Scratch Set and a Save Set. Any media in a Save Set cannot be overwritten until certain user-specified criteria are met. This prevents the possibility of inadvertently overwriting a tape before adequate backups or archives are preserved. After the user-specified criteria is met, the Save Set becomes a Scratch Set and is recycled to be used again (overwritten).
Once the media has passed certain specified criteria, such as a minimum number of media in the Save Set and a minimum retention period, the media is moved to the Scratch Set. The retention period is the number of days media is kept in the Save Set of a media pool. When these criteria are met, the media is moved from the Save Set to the Scratch Set and is made available for use.
The Media Pool Manager lets you create and maintain the Arcserve Backup media pools. Each media pool is assigned a name, and is organized according to serial numbers. The serial numbers assigned are permanent. If you use a device with a bar code reader, the bar code labels are used as the serial number of the media. Media pools are organized by the range of serial numbers of the media they contain. Media pools apply to every media, regardless of which backup or archive type and method were selected.
|
Copyright © 2016 |
|