

RAID 0, also referred to as "data striping," transparently distributes data over multiple drives to make them appear as a single, high-performance drive. This involves spreading out blocks of each file across multiple disks. Data striping uses parallel data processing to provide high throughput performance.
Although data striping provides high performance by allowing data to be processed in parallel, it does not provide fault tolerance. If a single drive in a RAID level 0 array fails, all data is lost; in the case of RAID tape drives, the backup is not available because of the drive failure.
RAID level 0 is an ideal solution when you require optimum throughput and fault tolerance is not an issue. If fault tolerance is required, you must use RAID level 1 or RAID level 5. The following diagram shows how data is distributed in a RAID 0 configuration:
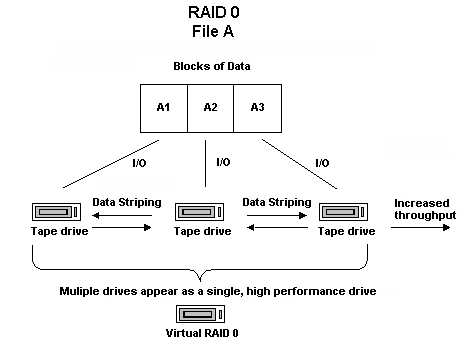
Note: Optimum performance is limited by the speed of the slowest drive in the array.
|
Copyright © 2016 |
|