

From a generated report, you can analyze the estimated RAM/Disk Space for future, based on multiple scans over a period of time in two methods.
Consider a scenario, where you need data values on your environment for a period of 31 days. Assume one scan per day for all the nodes in your environment and perform the scan for a period of 31 days.
You can generate the report using either of these methods:
First method:
The first method is to scan the data daily for few days and estimate the data based on the results of the scanned data. Scan the data daily for some days and estimate the data based on the results of the scanned data.
From the Scanned Volume Charts and Scanned Volume Details section, verify the details for memory, SSD, storage and other available options.
The calculation results in real estimation of data with graphs and values. This process is complex for you to run multiple scans across a long period of time.
Second method:
You can estimate the hardware requirements. Run the scan for couple of times for some days, then generate a report to get the estimated hardware requirements. When you perform a real scan for some days continuously, Arcserve UDP Data Store Capacity Planning Tool displays the values for Data changed per recovery point and estimates for rest of the days.
The following image displays the estimates for 31 days with 31 as the value for Number of Recovery Points to Retain: 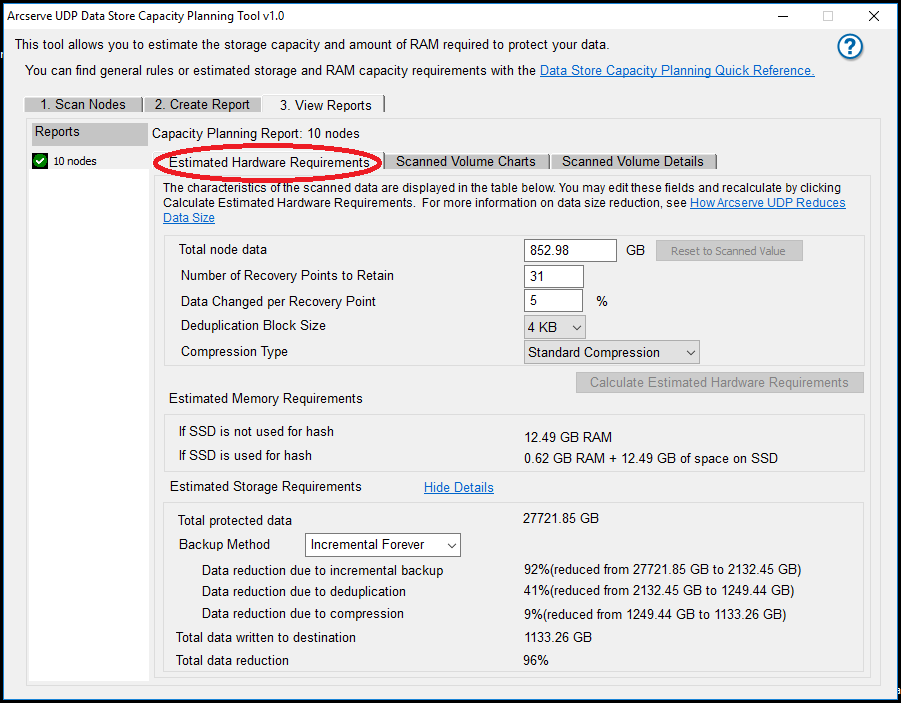
For number of node scans, the value of X is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and so on. When X is 2 or a value greater than 2, you have multiple node scan records. At this point of time Arcserve UDP Data Store Capacity Planning Tool calculates the value of Data Changed per Recovery Point. When the value of X increases, the value of Data Changed per Recovery Point is more accurate.
Note: When you perform only a single Node Scan, you do not get the value of Data Changed per Recovery Point. Then use 5% as a default value to estimate the hardware requirements.
Example:
The following steps help you calculate the Estimated Hardware requirements:
Total node data = size of volume C and D of node 1 + size of volume C of node 2 = (80 + 20) + 50 = 150GB from your point of view, this is the total valid data size on source nodes. By default, Arcserve UDP Data Store Capacity Planning Tool displays 31 as retained recovery points (considering 31 days data).
If you scan the nodes twice with a short time interval, it is highly possible that the Data Changed per Recovery Point is 0%.
In this example, let us assume that the Data Changed per Recovery Point is 5%.
In the example, let us assume that the deduplication percentage is 60% in case of 4 KB deduplication block size and compression percentage is 30% in case of standard compression.
Total protected data for 31 recovery points= (150 GB * 31) + (150 GB * 5% * 30) = 4875GB
Total data size after incremental backup for 31 recovery points: 150 GB + 150 GB * 5% * 30 = 375 GB
Data reduction from incremental backup: 92% (from 4875 GB to 375 GB)
Data size after deduplication: 375 GB * (1-60%) = 150 GB
Data reduction from deduplication: 60% (from 375 GB to 150 GB)
Data size after compression: 150 GB * (1-30%) = 105 GB
Data reduction from compression: 30% (from 150GB to 105GB)
Total data written to destination: 105 GB
Total data reduction: 98% (from 4875 GB to 105 GB)
Best efforts are taken by Arcserve UDP Data Store Capacity Planning Tool to make sure that the calculation is as accurate as possible, but be aware that the calculation is for Estimated Hardware Requirements.
The Data Changed per Recovery Point, Deduplication percentage and Compression percentage are calculated based on the scanned data. The future data might fetch different values. Even the total node data might fetch a different value when you calculate it in the future.
For this specific reason Arcserve UDP Data Store Capacity Planning Tool provides you an option to modify the values in multiple sections like Total node data, Number of recovery points to retain, Data change per recovery point and some other sections in Estimated hardware requirements tab.
|
Copyright © 2018 |
|