Destination Partition Options
The Restore Wizard offers various partition options for a selected disk:
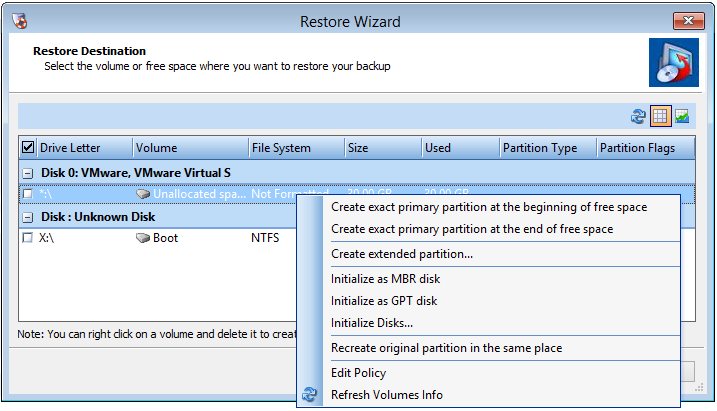
These options include:
|
Create exact primary partition at the beginning of free space |
(Available only if unpartitioned disk space exists) Creates a new primary partition on the destination disk of the same size as the source partition. The Wizard creates it at the start of unallocated space. Note: You cannot create more than four (4) primary partitions on an MBR disk. |
|
Create exact primary partition at the end of free space |
Creates a primary partition of the same size as the source partition in the disk's unpartitioned, unallocated space. The Wizard places the end of the new partition at the end of the unpartitioned space, then moves backwards to create a volume of the exact size as the original. |
|
Create extended partition |
(Available only on MBR drives and only if unpartitioned disk space exists on the drive.) Creates a new extended partition on the destination drive. This partition can then be divided into one or more logical drives or partitions. This allows more than four partitions on an MBR drive. |
|
Initialize as MBR disk |
Displays a list of available drives. Select one or more disks to initialize as an MBR disk. (Recovery Environment requires at least one initialized disk to restore the system/boot volume.) See Creating and Starting the Recovery Environment for details. |
|
Initialize as GPT disk |
Displays a list of available drives. Select one or more disks to initialize as a GPT disk. (Recovery Environment requires at least one initialized disk to restore the system/boot volume.) See Creating and Starting the Recovery Environment for details. |
|
Initialize Disks... |
Displays a list of available drives. Select one or more disks to initialize as either MBR or GPT. (Recovery Environment requires at least one initialized disk to restore the system/boot volume.) See Creating and Starting the Recovery Environment for details. |
|
Recreate original partition in the same place |
Creates a duplicate of a single partition at the same location as the original on the new drive. |
|
Edit Policy |
Runs the Partition Policy Editor for changing partition alignment and offsets. For example, use the Editor for restoring a hard disk volume to an SSD for Windows system volumes prior to Vista. |
|
Refresh Volumes Info |
Asks the operating system for more current data on the drive volumes. |
The Partition Restoration Scenarios section illustrates these different configurations.
This section contains the following topics: