CA ARCserve D2D allows you to not only protect and recover your data, but also helps you to get the Microsoft Exchange Server application that uses that data back up and running. The Microsoft Exchange Server recovery can only be made using the Restore by Recovery Point method.
|
|
|
|
CA Support: |
|
|
YouTube: |
|
CA ARCserve D2D supports the following versions of Microsoft Exchange Server:
For Exchange 2007 CCR environment, CA ARCserve D2D must be installed on both the active node and passive node of Microsoft Cluster. Backup can be performed from an active node and passive node, but restore can only be performed to an active node.
For Exchange 2010 DAG environment, CA ARCserve D2D must be installed on all member servers in the DAG group. A backup job can also be performed from any member server for both active and passive database copies, but restore can only be performed to an active database copy.
Note: Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 Cluster Environment and Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 Single Copy Cluster (SCC) environment are not supported by CA ARCserve D2D.
Microsoft Exchange Server can be restored at the following levels:
If you want to restore all the Microsoft Exchange Server data, you can perform a restore at Microsoft Exchange Writer level.
If you want to restore a specific Storage Group, you can perform a restore at the Microsoft Exchange Storage Group level.
(Does not apply for Microsoft Exchange Server 2010).
If you want to restore a specific Mailbox Store, you can perform a restore at the Mailbox Store level.
If you want to restore a specific Mailbox Database, you can perform a restore at the Mailbox Database level.
Restore Microsoft Exchange Server Application
Note: When performing a Microsoft Exchange Server database restore (to either the original location or a recovery storage group/recovery database), you must verify that the account also has the following administrative privileges:
The restore methods selection dialog opens.
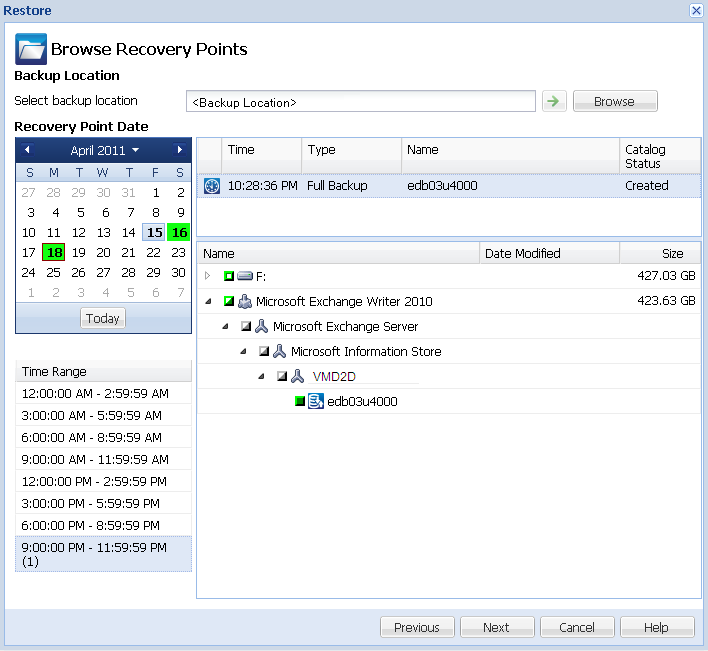
The Browse Recovery Points dialog opens.
The corresponding marker box becomes filled (green) to indicate that the database has been selected for the restore.
Note: If you do not want the transaction log files to be applied after the restore, you must manually delete it before the restore is performed. For more information about manually deleting transaction log files, refer to the Microsoft Exchange Server documentation.
The Restore Options dialog opens.
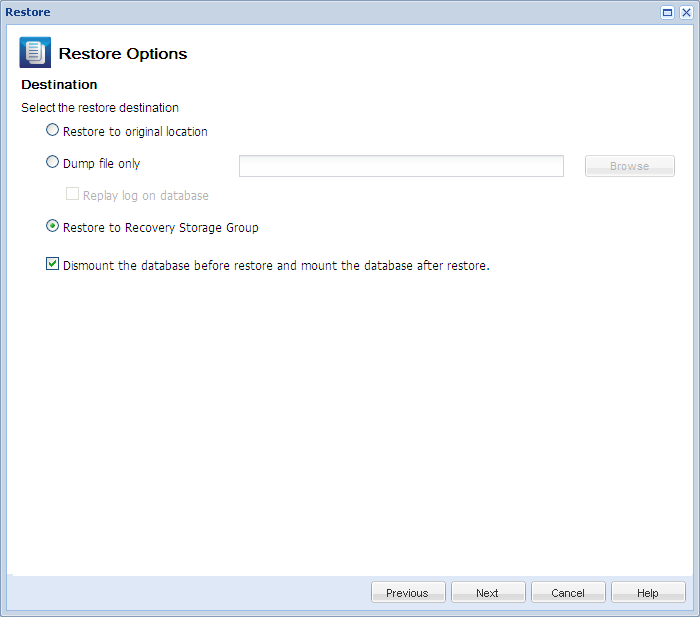
The available options are to restore to the original location of the backup, restore the dump file only, or restore to a Recovery Storage Group/Recovery Mailbox Database.
Restores to the original location from where the backup image was captured.
Restores the dump files only.
For this option, CA ARCserve D2D will restore the Microsoft Exchange database file to a specified folder, and will not bring it online after recovery. You can then move this file to a different server and mount it to exchange server manually to view data contained in it.
Note: When a Recovery Mailbox Database exists, restore with ‘Dump file only’ option will fail.
Specifies that when the database files are dumped to the destination folder, you can replay and apply all Microsoft Exchange transaction log files and commit them to the database file. When the database next starts, and transaction log files that were not yet written to the database files are then applied before the database is again made available to you.
Note: This option is not applicable for Microsoft Exchange Server 2003
Restores the database to a Recovery Storage Group (RSG).
An RSG is a storage group that can be used for recovery purposes. You can restore a Microsoft Exchange Mailbox Database from a backup in a Recovery Storage Group and then recover and extract data from it, without affecting the production database that is being accessed by end users.
Before restoring an Exchange 2007 database to a Recovery Storage Group, you must create a Recovery Storage Group and Mailbox Database with the same name.
For example, if you want to restore MailboxDatabase1 from the First Storage Group to a Recovery Storage Group, you must create a Recovery Storage Group and add the database "MailboxDatabase1" to the Recovery Storage Group.
Note: This option is not applicable for Microsoft Exchange Server 2003
Typically before a restore, Microsoft Exchange will perform some checks to help ensure the following:
To protect a Microsoft Exchange production database from being restored unexpectedly, a switch is added to allow the database to be overwritten during the restore process. Microsoft Exchange will refuse to restore a database if this switch is not set.
For CA ARCserve D2D, these two options are controlled by this "Dismount the database before restore and mount the database after restore" option. With this option, CA ARCserve D2D lets you launch the restore process automatically without any manual operations. (You can also specify to dismount/mount database manually).
The Exchange administrator would have to perform some manual operations such as dismount the Exchange database, set the Allow Overwrite flag on the database, and mount the Exchange database. (The recovery procedure is performed by Exchange during the mounting of the database).
In addition, if unchecked, this option does not allow the Exchange database to be overwritten during restore.
Restores the database to a Recovery Database. A Recovery Database is a database that can be used for recovery purposes. You can restore a Microsoft Exchange Mailbox Database from a backup to a Recovery Database and then recover and extract data from it, without affecting the production database that is being accessed by end users.
Before restoring an Exchange 2010 database to a Recovery Database, you must first create a Recovery Database.
Note: This option is not applicable for Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 and 2007.
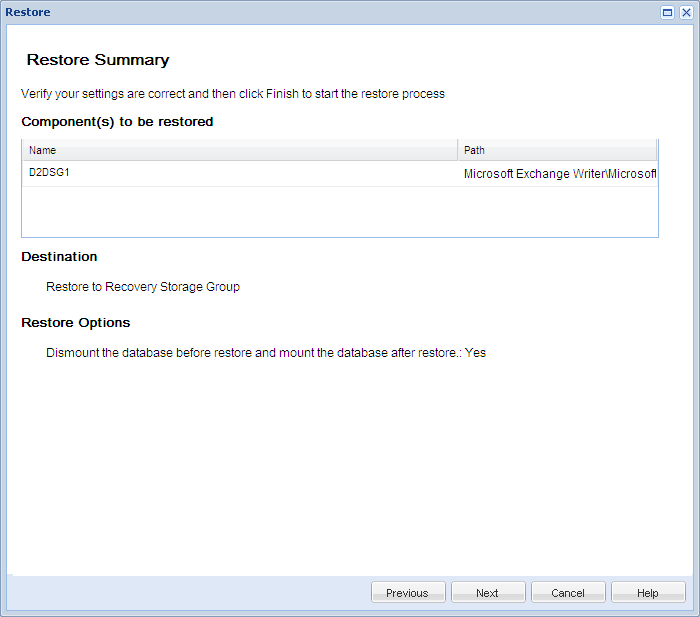
The Restore Summary dialog opens.
| Copyright © 2012 CA. All rights reserved. |
|