

Each time Arcserve UDP Agent (Windows) performs a successful backup, a point-in-time snapshot image of your backup is also created. Before creating a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) file from an Arcserve UDP Agent (Windows) backup, you must have at least one Arcserve UDP Agent (Windows) recovery point available.
Follow these steps:
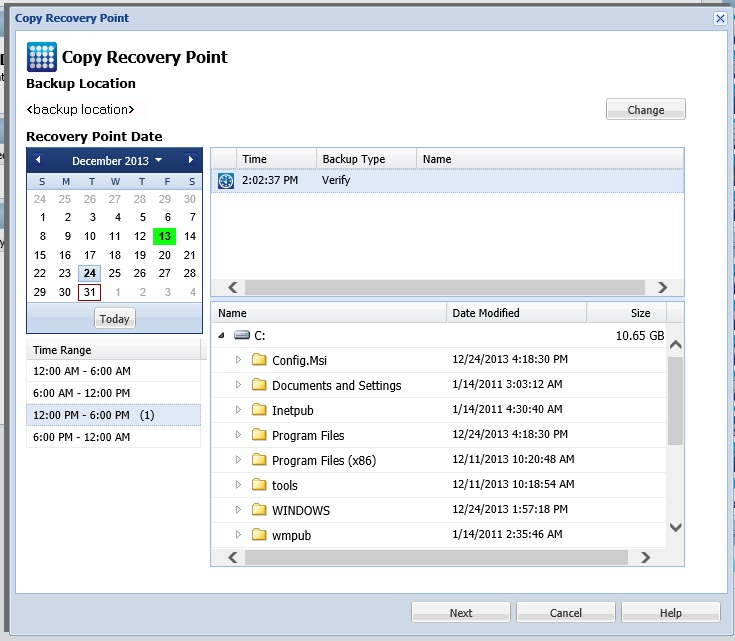
The Copy Recovery Point dialog opens.
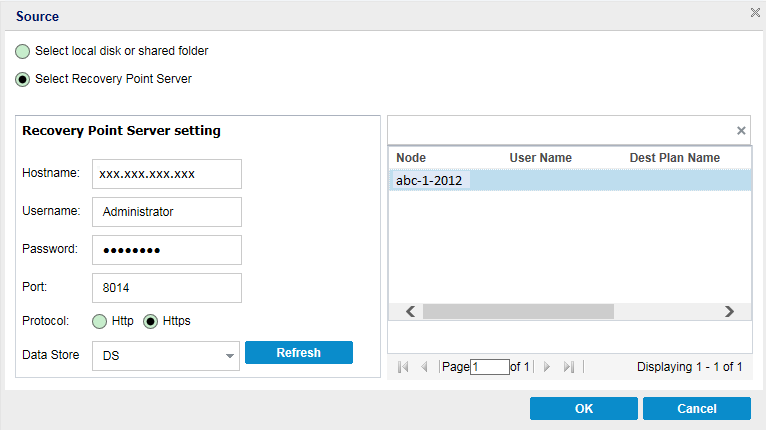
The Source dialog opens where you can select the backup location.
Select local disk or shared folder
a. Specify or browse to the location where your backup images are stored and select the appropriate backup source.
You can click the green arrow button to verify the connection to the specified location. If necessary, enter the Username and Password credentials to gain access to that source location.
The Select backup location dialog opens.
b. Select the folder where the recovery points are stored and click OK.
The Select backup location dialog closes and you can see the backup location in the Source dialog.
c. Click OK.
The recovery points are listed in the Browse Recovery Points dialog.
Select Recovery Point Server
a. Specify the Recovery Point Server setting details and click Refresh.
All the agents are listed in the Data Protection Agent column in the Source dialog.
b. Select the agent from the displayed list and click OK.
The recovery points are listed in the Browse Recovery Points dialog.
Note: All the dates containing recovery points for the specified location are highlighted in green.
The corresponding recovery points for that date are displayed, with the time of the backup, the type of backup that was performed, and the name of the backup.
The corresponding backup content (including any applications) for that recovery point is displayed.
Note: Verify that you select a location that has sufficient free space available to hold the entire VHD.
Compression is not performed. Files are converted to .vhd format directly, without the need for manual operations. This option has the lowest CPU usage (fastest speed), but also has the highest disk space usage for your backup image.
A status notification window appears and the copy process for the selected recovery point type is launched immediately.
The recovery point image is copied from the backup source to the destination.
"VStore\S0000000001"
For example, if your computer name is "Department_A" and you copied the recovery point (backup) to "E:\export_vhd\" you would navigate to:
E:\export_vhd\Department_A\VStore\S0000000001
Each of these files corresponds to an actual physical disk on the source computer which can be used as regular VHD files.
Important! The VHD created by Arcserve UDP Agent (Windows) during the copy process may not boot in the hypervisor because the VHD files may not contain the correct drivers for the VM.
|
Copyright © 2016 |
|